
High-pass filters are an essential tool in the world of audio production and signal processing. They are used to remove low-frequency content from a signal, allowing the higher frequencies to pass through unaffected. This can be useful in a wide range of applications, from cleaning up audio recordings to enhancing the clarity of a musical performance. In this blog post, we will explore what a high-pass filter is, how it works, and some of its applications.
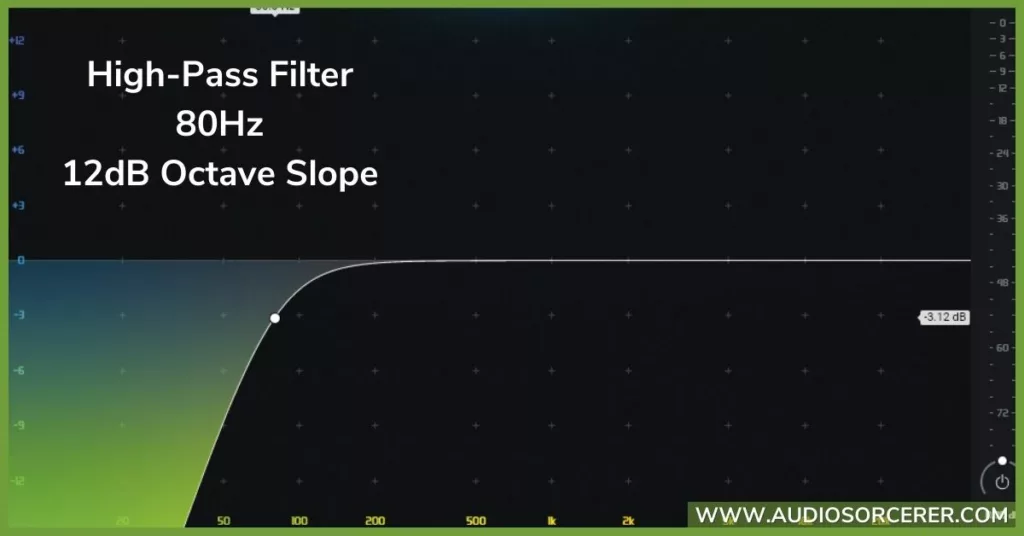
A high-pass filter, not to be confused with a low-cut filter, is an electronic circuit that allows high-frequency signals to pass through while blocking low-frequencies. This is achieved by using a combination of resistors, capacitors, and sometimes inductors, which work together to create a filtering effect.
The circuitry of a high-pass filter is designed to pass frequencies above a certain point, known as the cutoff frequency. Audio below this certain cutoff frequency is attenuated, meaning it is reduced in amplitude or removed entirely from the signal.
High-pass filters can be found in many different types of audio equipment, including mixing consoles, equalizers, and microphone preamplifiers. They are also commonly used within audio plugins and software for mixing and mastering. You would be hard-pressed to find a mix that hasn't utilized a high-pass filter to help shape it.
To understand how a high-pass filter works, it's helpful to first understand the basic principles of capacitors and resistors. Capacitors are electrical components that store energy in an electric field, while resistors are components that resist the flow of electrical current.
In a high-pass filter, the capacitor and resistor work together to create a filtering effect. When an audio signal is passed through the circuit, the capacitor blocks low-frequencies by storing up the charge and preventing it from passing through to the output. At the same time, the resistor allows high-frequency content to pass through to the output.
The amount of high-frequency content that is allowed to pass through the filter is determined by the values of the capacitor and resistor, as well as the cutoff frequency of the filter. The cutoff frequency is the point at which the high-pass filter begins to attenuate the low-frequencies. The higher the cutoff frequencies are, the more low-frequency content will be attenuated by the filter.
The basic formula for calculating the cutoff frequency of a high-pass filter is:
Fc = 1 / (2πRC)
Fc is the cutoff frequency of the audio filter, R is the resistance of the resistor, and C is the capacitance of the capacitor. This formula can be used to determine the cutoff frequency of a high-pass filter given the values of the resistor and capacitor.
High-pass filters can be used in a wide range of applications, from cleaning up audio recordings to shaping the sound of individual tracks in a musical performance. Here are some of the most common applications of high-pass filters.
When you high pass filter audio, the low end information in audio recordings gets cleaned up. When recording audio, it's not uncommon to pick up unwanted low-frequency noise, such as hum from electrical equipment or vocal plosives. By using a high-pass filter to remove this low-frequency content, the recording can be cleaned up and made to sound much clearer.
Learn about low-frequencies and the Proximity Effect in vocal recording. CLICK HERE

In a live musical performance or recording, it's not uncommon for different instruments to compete for the same range in a frequency spectrum. This can make it difficult to hear and distinguish individual sounds. By using high-pass filters to remove some of the low-frequencies from each instrument, the clarity of the performance can be enhanced, allowing each instrument to be heard more clearly.
High-pass filters are most commonly used in equalizers, which are used to adjust the balance of different frequency ranges in a signal. By using high-pass filters to remove low-frequency content, the balance of the signal can be adjusted to emphasize or de-emphasize certain frequency ranges. For example, a high-pass filter might be used to remove some of the bass frequencies from a guitar track, making it sound thinner and more treble-heavy.
In electronic music production and DJ equipment, high-pass filters are often used to shape the sound of individual tracks or entire mixes. By using high-pass filters to remove some of the low-frequency content from a track, the DJ can create a buildup of tension that is released when the full bass frequencies are reintroduced. This can be a powerful tool for creating energy and excitement on the dance floor.

High-pass filters can also be used to protect speakers from damage caused by very low frequencies. When a speaker is driven too hard by low-frequencies, it can be damaged or even destroyed. By using a high-pass filter to remove some of the extraneous low frequencies from the signal before it reaches the speaker, the risk of damage is reduced.
Related Article: EQ Cheat Sheet | The Only Guide You'll Ever Need!
Now that you've learned what a high-pass filter is, does, and some of its use cases, let me give you 3 tips to use one like a pro.
Vocals: A high-pass filter is almost always used when mixing vocals. Depending on whether it is a female or male vocalist, that will usually determine how high the cutoff point will be. A good starting place is between 100Hz and 200Hz. Use your ears to find the frequency where the vocal starts to thin out but doesn't lose its fullness.
Snare Drum: Cleaning out the low end of a snare is important so that it doesn't interfere with bass heavy instruments. That low end of a snare is actually higher than many think. 100Hz to 240Hz will give the snare the power it needs to sound thunderous in a mix. With that being said, use a high-pass filter between 80Hz and 100Hz.
Full Mix: You should always use a high-pass filter on your overall mix or master. Cleaning out the sub low frequencies will allow you to achieve louder masters. I recommend 20Hz up to 40Hz. This is genre dependent and for bass heavy songs 20Hz is ideal.
TIP: Use a 12dB octave slope for most applications.
Though a high-pass filter is probably the most popular and used, there are 3 other audio pass filters you can utilize to help create better mixes. Let's look at the low-pass filter first.
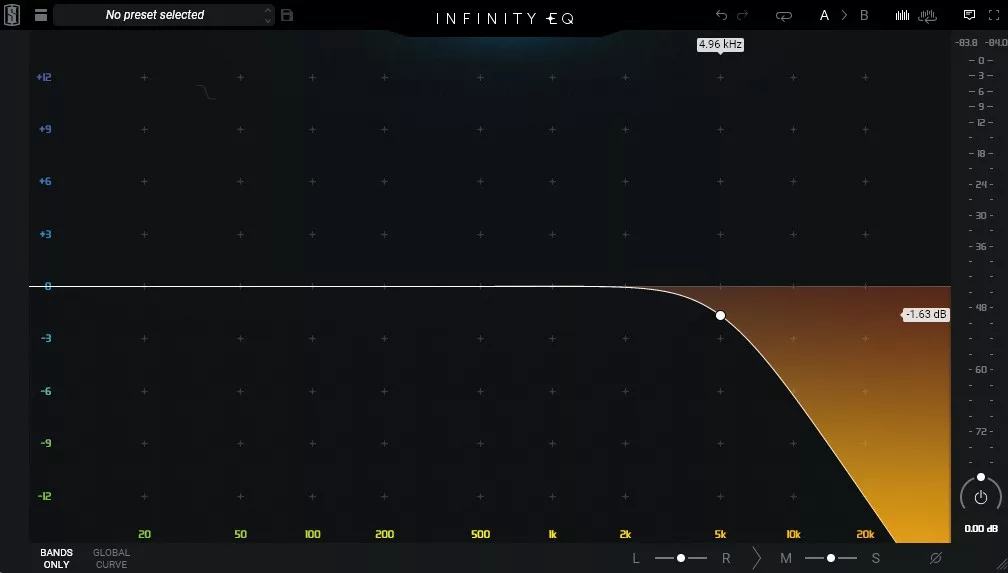
Low-pass filters are an electronic circuit or signal processing technique that allow low-frequency signals to pass through while attenuating or blocking high-frequencies. It is called a low-pass filter because it passes signals with frequencies lower than a certain cutoff frequency, while attenuating or blocking frequencies above the cutoff frequency.
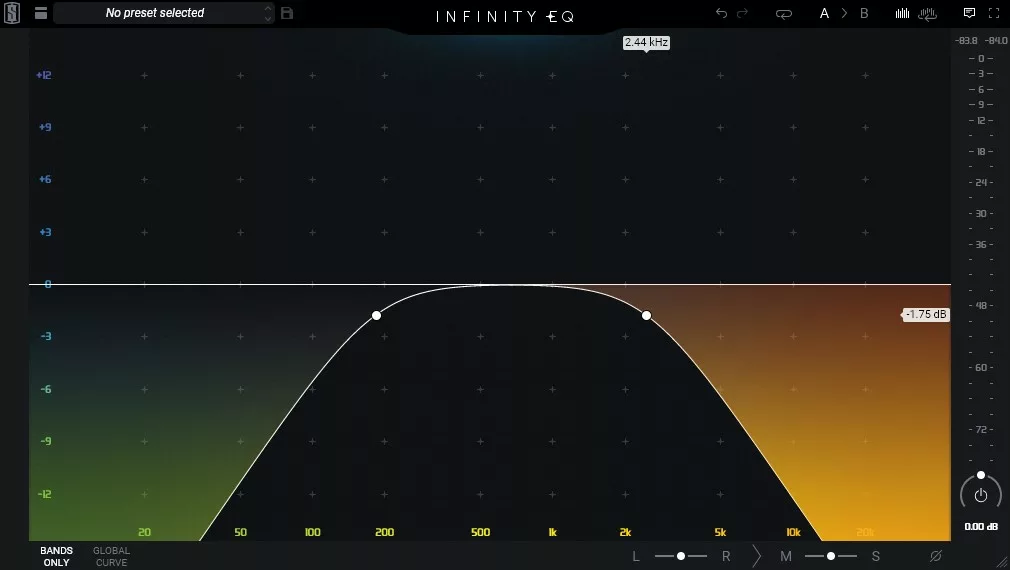
Band-pass filters are an electronic circuit or signal processing technique that allows a specific range of frequencies to pass through while attenuating or blocking frequencies outside that range. It is called a band-pass filter because it passes signals within a certain frequency band, while attenuating or blocking frequencies outside the band.
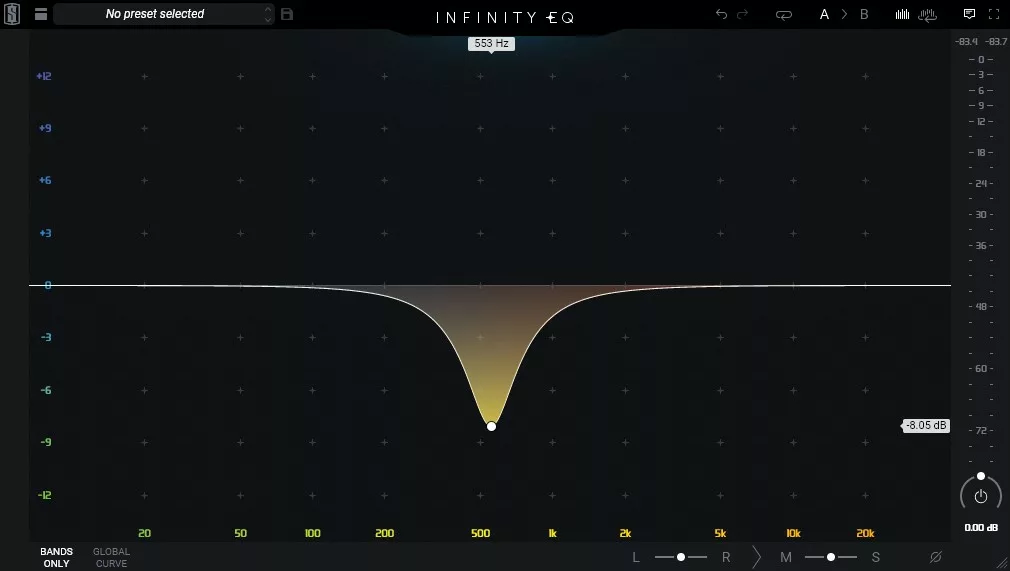
A notch filter is an electronic circuit or signal processing technique that attenuates or blocks a specific frequency range, while allowing frequencies outside the range to pass through. It is also known as a band-stop filter because it stops or attenuates a narrow band of frequencies centered around a specific frequency, while allowing frequencies above and below this band to pass through unaltered.
In conclusion, a high-pass filter is an essential tool in the world of audio production and signal processing. By allowing high-frequencies to pass through while blocking low-frequency content, a high-pass filter can be used to clean up audio recordings, enhance the clarity of musical performances, shape the sound of individual tracks, protect speakers from damage, and more.
Whether you're a professional audio engineer, a DJ, or a hobbyist musician, understanding high-pass filters and how they work is an important part of creating high-quality audio. Using high-pass filters to shape the sound of your recordings and performances, you can achieve a cleaner, clearer, and more professional sound that will stand out from the crowd.
"Some of the links within this article are affiliate links. These links are from various companies such as Amazon. This means if you click on any of these links and purchase the item or service, I will receive an affiliate commission. This is at no cost to you and the money gets invested back into Audio Sorcerer LLC."